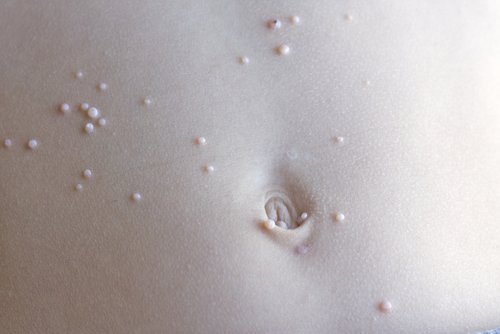
Molluscum Contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a contagious skin condition caused by a viral infection. The molluscum virus is a pox virus that causes skin lesions in both children and adults, though it is far more common in children. The virus is spread by contact with affected skin or contact with objects with the virus on it, such as towels and washcloths. It can even be spread sexually. Also, people with suppressed immune systems can develop much more severe and long-lasting infections.
Molluscum appears as small, dome-shaped bumps on the skin. The bumps usually have a small dimple in the center, and they range in size from the size of a pinhead to just smaller than a pencil eraser. They can be skin-colored or white in color. Although the bumps can appear anywhere on the skin, they usually do not affect the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet. Typically molluscum do not itch or hurt, but sometimes a dermatitis (itchy rash) can develop around the bumps causing some itchiness and discomfort. The diagnosis can be made with an in-person evaluation and a biopsy is usually not needed.
To prevent the molluscum virus from spreading to other areas of the body and other people, we recommend:
Avoid scratching or touching the bumps
Avoid sharing towels, washcloths, razors, or other personal equipment
Avoid any close skin-to-skin contact until the lesions have healed
In healthy people, the molluscum virus will eventually resolve on its own without treatment. But it can often take months to over a year. If you are concerned about molluscum contagiosum or any other skin changes, please visit a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment.